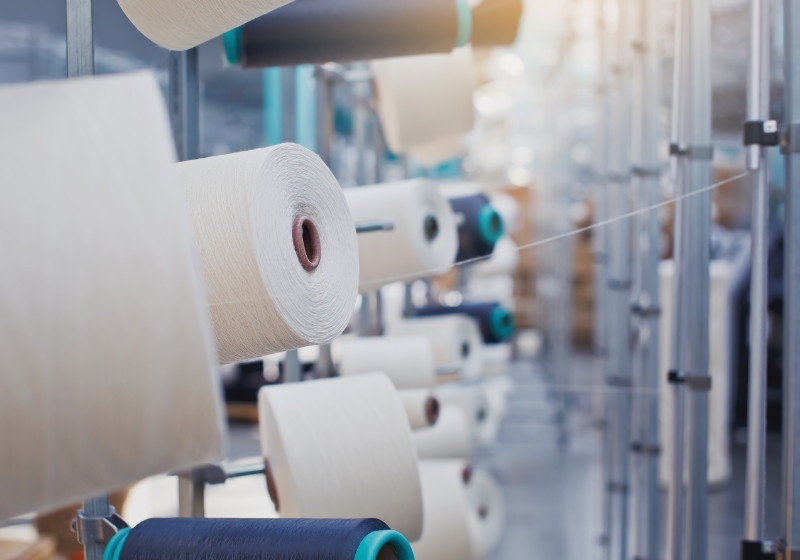
STOCKHOLM – A new life-cycle assessment on a post-consumer textile fibre-to-fibre recycling method that uses urea to dissolve cellulose instead of the usual harsh chemical carbon disulphide has highlighted some key environmental savings.
The researchers concluded that dependent on the energy mix, and compared to conventional viscose and cotton fibre production, the impacts of using cellulose carbamate technology to process post-consumer textiles into fibre can decrease impacts related to climate, water scarcity, cumulative energy, and land use.
Finnish innovator Infinited Fiber uses carbamate fibre technology in its production process and this LCA builds on primary data collected from the company.